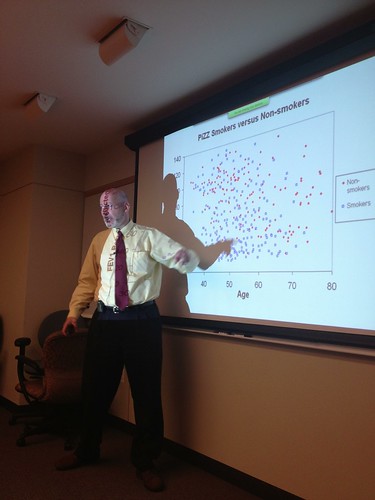
Dr. Ed Silverman, Professor of Medicine and Chief of the Channing Division of Network Medicine gave a broad and fascinating tour of respiratory physiology and the underlying population genetics.
Friday, June 21, 2013
Friday, May 17, 2013
Profiles—A Tool to Study Researcher Communities
Griffin Weber described the Profiles open source tool that is now being used world wide that was first developed for our work in Harvard Catalyst. It is used to find collaborators, create teams for research projects, study promotion and the processes of academia.
Death and its predictors
Professor Tianxi Cai ran a very interesting discussion about generating risk profiles for biomarkers and the problem in adjusting out the diseases that are along the causal pathway to mortality of those biomarkers. As a result of such an over adjustment, most biomarkers will give counter-conventional-wisdom associations.
Friday, May 10, 2013
Governance models for distributed queries across heterogeneous healthcare institutions
Murphy, Bickel, Kohane, Simons, Churchill, Mendis. Wattanasin, Weber, Donahoe, MacFadden
Discussed the interaction between different governance models and how they interact with the architecture.
Wednesday, April 10, 2013
Friday, April 5, 2013
Characterizing Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) in the EHR
Profs Cai and Shaw led a discussion of the the CAD NLP algorithm and demonstrated how the different priors and different ascertainment biases of different clinics could affect the accuracy of the NLP classification. Also discussed counter-intuitive coefficients in the model which may reflect confounding by the treatments for CAD.
NLP
Guergana's team: discussed speed issues.
cTAKES with full UMLS module takes about 150 notes/hour/core. Discussed various architectural tradeoffs.
Friday, March 15, 2013
All Hands Meeting Ps
10:14 AM, Mar 15, 2013
Jordan Smoller, co-PI of the MDD-SSRI-resistance i2b2 DBP presented today the paper he contributed to that made a lot of headlines regarding genomic variants shared across 5 psychiatric disorders.
Accelerating NLP
Tianxi Cai led a discussion of "Semi Automated Model Building Using Knowledge Bases" using bibliographic external sources of medical knowledge to generate the candidate terms for a NLP filter to phenotype a particular characteristic.
Friday, February 1, 2013
Inflammation DBP
Tianxi Cai led a discussion of how to discretize (or not) some of the parameters across our various disease populations regarding inflammatory burden. Also determination of whether we use the study population to establish the reference range or use the larger "official" reference ranges. Szolovits quoted the wonderful paper: The haze of Bayes, the aerial palaces of decision analysis, and the computerized Ouija board.
Friday, January 11, 2013
Epigenetic states and outcome
Professor Tianxi Cai led a discussion on the study designs to relate epigenetic endopathotypes and clinical outcomes.
Annotation of clinical notes
Guergana led a discussion of the user interface challenges of term selection (in an annotation of a clinical document task). She re-introduced the crew to the UMLS and Concept Unique Identifiers (CUIs). Understanding the dependencies, as Shawn Murphy pointed out is critical to providing users just the right set of terms to pick from (too many terms includes too many irrelevant terms and distracts/consumes the user and too few terms cripples expressivity). So we recognize that knowledge of the UMLS and the medical task is going to be required to optimally select the right set of CUI's to identify patients of interest. Sheng Yu demonstrated work in collaboration with Tianxi Cai that is quite striking in its ability to use the patient corpus to select (rank highly in a pick list) the CUI's of greatest relevance.
Friday, January 4, 2013
NLP games
Cai, Savova et al.
Discussed tradeoffs between performing string matching (hard to scale to the general case, but quite adequate accuracy for well specified and specific narrow cases) and general NLP. Also discussed how to enrich prior probability for a disease of interest to increase performance of high specificity NLP.